An outdoor bicycling workout is performed in a low gear on a flat road to get those slim cyclist legs. The difference with a hill workout is that your body contracts the legs more frequently which leads to muscle toning. Nutrition Proper nutrition provides athletes with the energy, nutrients and hydration they need to progress in their training and perform optimally. In addition to following a healthy diet, athletes must pay particular attention to gaining muscle and losing fat, which together improve athletic performance. To power workouts and games, and to ensure a strong recovery, elite athletes take care to eat properly and to hydrate before, during and after workouts and competitions. In some situations, athletes gain an edge with prescribed use of safe supplements.

Once you experience something you will know if it’s right for you. One of the greatest influences on how you build leg muscles during cycling is how you ride. If you’re chugging up single-track trails on your mountain bike, you’ll be building muscle at a far faster rate , than if you were taking a spin around the park. When it comes to packing on size, you need to do a lot more than cycling to get those monster quads and killer hamstrings you’ve been working towards. To experience muscle hypertrophy in your legs, you need to participate in a strength training program specifically designed for building muscle mass. The vast majority of Americans can experience significant health benefits from performing Peloton workouts on a regular basis.
I started out as a roadie myself and I had pretty good quad development back then. Squats, lunges, step ups, calf raises, leg curls, and such. A regular road bike would have at least a few gears allowing you to start from a lower one and go higher as the speed increases. A track bike does not offer similar options since fixed gear systems are faster in the long run.
Then as time goes on maybe add more resistance and lower your cadence to 85rpm. Doing this for myself personal has caused no increased knee pain, but if I go all out high resistance, I have terrible pain while riding and even worse after. This may or may not answer your actual question, but I thought I’d at least share what works for me.
There are a magnitude of things cycling does to your legs over time and increasing leg size greatly is not one of them. There are many benefits to cycling and what cycling does to your legs over time. Jennifer Rowan is an adventure writer, covering outdoor fitness activities of all kinds, from hiking and biking to snowboarding and surfing.
Table of Contents
Body Type Plays A Huge Role
By far, your quads and hamstrings are the two muscle groups that work the hardest when you cycle. Every time you push down on your pedal, you engage those muscles. Your calf muscles, too, are getting a workout as they help with the overall pushing effort, and especially come into play when you’re out of the saddle and pushing uphill.

Now this should be taken with caution, for any endurance athlete , dangerously cutting calories is never good for your health. Experiment with small incremental reductions until you hit that sweet spot between ‘still not losing weight’ and ‘losing weight but performance is seriously going downhill’. When you do cut, cut the carbs, your body will begin to eat excess muscle when it runs out of fuel. Indoor cycling, or spinning, makes your thighs bulky. Finally, there are a couple of supplements that may help you out – neither will build muscle on their own, but they can facilitate the process when combined with exercise.
Think of long distance runners vs short distance runners. Below is an image of an elite female track cyclist under the name of Tammy Thomas. According to the official information, she tested positive for steroids in 2002.
Our Training Plans
Women have much lower levels of testosterone than men (around 15% less), and higher levels of body fat (around 10% more). The body fat is necessary for a healthy menstrual cycle and it’s just the way we are. You think the guys and gals on the velodrome just ride their bikes all day? Keep your muscles long and lean by stretching after your ride. Your quadriceps and hamstrings work to push and pull your pedals around.

Check out hockey drills and workouts from goaltender Jean-Sebastien Giguere, defenseman Duncan Keith, the University of Michigan hockey team and others. Cool down from riding your bike by pedaling slowly for five to 10 minutes to give your heart rate time to slow down. They are typically very thin, but that is because they require the use of slow twitch fibers over fast twitch for their sport. Just like with how you run (compare a sprinters’ legs with long-distance runners).
If your training routine consists of frequent rides lasting longer than one hour, you could potentially burn over 600 calories each time you head out on your bike. Your calves are constantly being flexed and abducted while cycling, so carrying out calf raises on rest days mimics the action this muscle makes on a bike, building its strength further. Lunging engages your quads, hamstrings, glutes and calf muscles so they are an excellent all-round exercise for improving leg strength. They also help iron out any minor imbalances in thigh strength. While cardiovascular fitness is a must for high-level cycling, improved leg strength can help with a more balanced physique. Gradually increase your exercise with an aim to performing an hour of aerobic exercise most days of the week to make your body more efficient at burning fat.
Pedaling, especially uphill, extensively works your thighs, hamstrings, and butt, all areas that are mostly influenced by cellulite. Sports News Latest sports news, for all pro sports, college sports, high school sports, and more. College Recruiting The athletic recruiting process is a lot like dating, with college coaches/scouts and high-school student-athletes sizing each other up and searching for the right match. Learn best practices from athletes who have achieved success and the experts who have helped them.

Women, with their almost negligible amounts of testosterone, won’t bulk up nearly as much. Every year you may catch a glimpse of the Tour de France on TV or you may notice the road cyclists that hit your local byways in packs of wild colors on the weekends as they log mile after mile on their bikes. But the one thing you probably won’t see much of are bulky legs. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, a 154-pound person can burn anywhere between 145 and 295 calories per 30-minutes of bike riding.
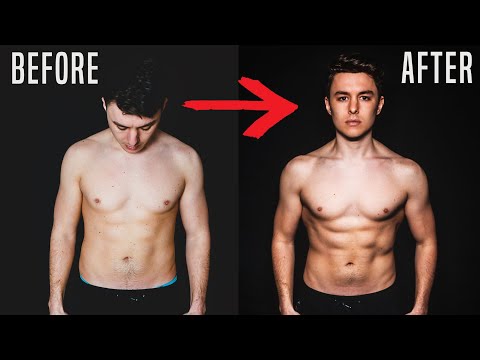
If this is your body type, don’t “fear” the muscle, embrace it and use it to your advantage on the bike. The exercise bike does not automatically give you big legs. However, if you go about your biking routine and eating routine wrong, you could end up with large, broad hips and thighs. That does not mean you need to give up your bike; instead, understand which workouts you should choose. That’s why sprinters, who routinely hammer monster gears, develop tree-trunk quads over time.

Your body type plays a role into how you carry your weight. You may be able to develop muscle fast or you might naturally have a leaner build. A more muscular frame may develop more muscle from riding a bike. However, the average bike rider, whether you commute or ride for cardio, will not get bulky legs.



